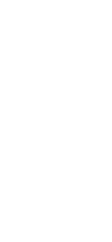
T-cells, a type of lymphocyte, are
collected from the blood of donors and recipients using the apheresis method. By co-culturing T-cells and anti-human CD80/CD86 antibodies from donors and recipients, inducible inhibitory T-cells
(JB-101) are prepared as cells such that
the patient’s body does not reject the
tissues of organs transplanted from
donors.
*Apheresis method:
A method for separating plasma components and cell components in blood obtained by extracorporeal circulation.
Inducible inhibitory T-cells (JB-101) are administered after the organs are transplanted into patients. After administration, while confirming the
patient’s safety, the immunosuppressant dose is gradually reduced. During this
time, monitoring is performed to ensure
that occult rejection does not occur.
Finally, immune tolerance is achieved
when immunosuppressant administration
is discontinued.
*Immune tolerance:
Discontinuation of immunosuppressant administration.
Inducible inhibitory T-cells (JB-101) are administered after organs are
transplanted into recipients. After administration, while confirming the
patient’s safety, the immunosuppressant dose is gradually reduced. During this
time, monitoring is performed to ensure
that occult rejection does not occur.
Finally, immune tolerance is achieved
when immunosuppressant administration
is discontinued.
*Antigens:
Tissues, cells, and viruses, etc., that enter a living body from the outside.
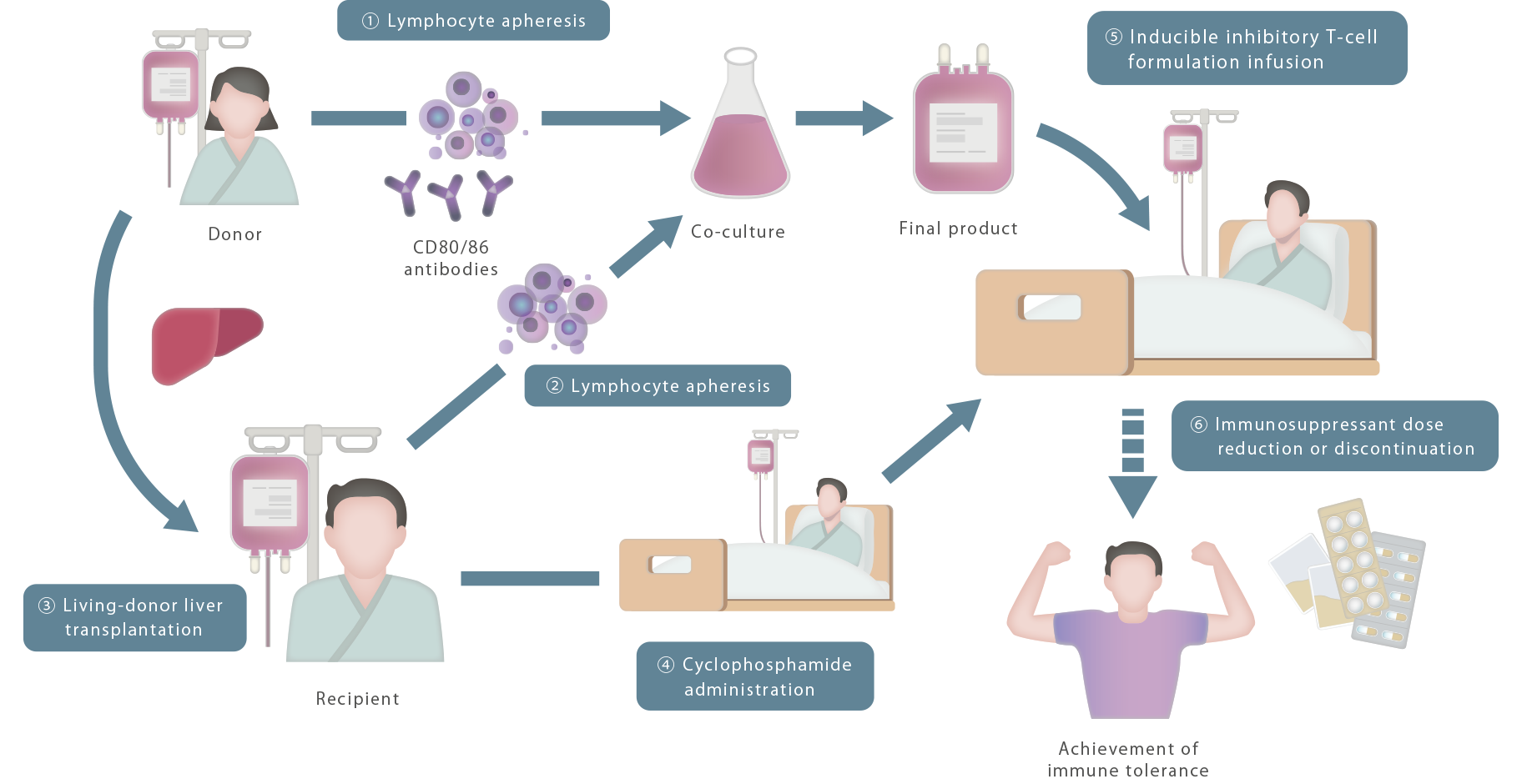
In 1971, Ko Okumura, a specially
appointed lecturer at Juntendo University, found suppressor T-cells,
which are cells
that suppress immunity. After this, the Juntendo University research group has studied the mechanism
of immune
rejection in the body, and thus succeeded
in preparing inducible inhibitory T-cells.
Next, focusing mainly on the rejection of organ transplants, which is a form of hyperimmune reaction, non-clinical
studies were performed with mice and monkeys. Then in 2016, in clinical
research at Hokkaido University,
living-donor liver transplantation was performed using inducible inhibitory
T-cells. With 7 of the 10 liver transplant patients, complete discontinuation of
immunosuppressant administration was successfully achieved.
JUNTEN BIO was established in order to make practical use of the results of
research by the Juntendo University research group,
and thus to develop pharmaceutical products.
Our further aim
is to expand from organ transplantation to research on intractable diseases due to hyperimmune reactions..

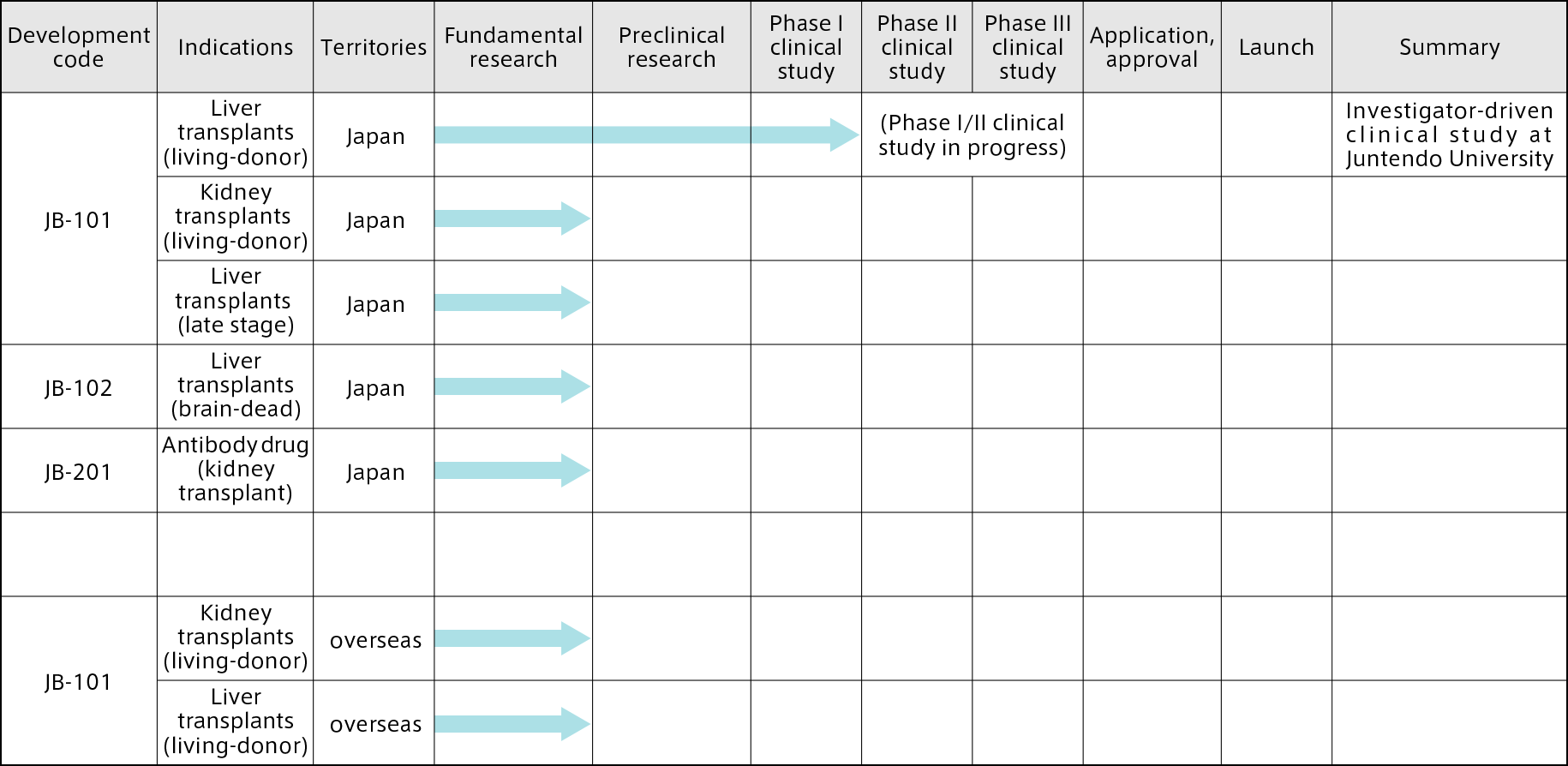
Planned development themes
In June 2020, inducible inhibitory T-cells
(JB-101) were designated as a product to
be included in the Ministry of Health,
Labour and Welfare’s (MHLW’s) system of expedited reviews aiming to make Japan
the world’s leader in the application of innovative medicine.
In July 2020, Juntendo University
submitted to the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency a clinical trial notification for a “Phase I/II clinical study to evaluate the capacity of inducible
inhibitory T-cells (JB-101) to induce
immune tolerance in living-donor liver transplant patients, and the safety of this treatment,” and started an
investigator-initiated study with the aim of achieving more widespread use of liver transplantation without the need for immunosuppressants.
Our future aim is to expand the
indications and progress with clinical
studies overseas, as shown in the
following table of planned development themes.